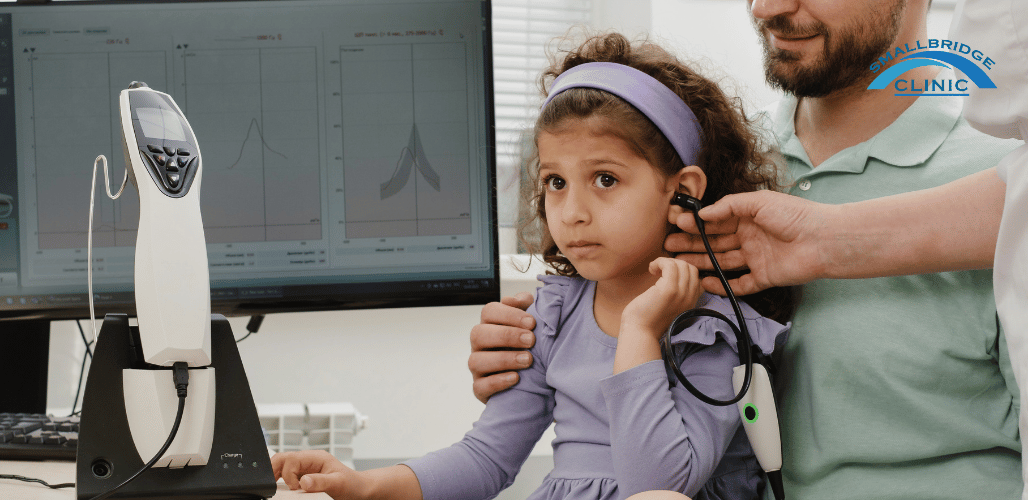
Hearing Tests and Hearing Aids Fitting Services
Types of Hearing Tests
-
Pure-Tone Audiometry:
- Air Conduction Testing: Uses headphones to deliver sounds at various pitches and volumes to each ear. Patients indicate when they hear a sound, helping to determine the quietest sounds they can hear at different frequencies.
- Bone Conduction Testing: Involves a small device placed behind the ear that sends sound directly to the inner ear through the bones of the skull, bypassing the outer and middle ear. This helps identify where the hearing loss is occurring.
-
Speech Audiometry:
- Speech Reception Threshold (SRT): Determines the lowest level at which a patient can understand speech.
- Word Recognition Score (WRS): Measures how well a patient can recognize and repeat words at a comfortable volume level.
-
Tympanometry:
- Assesses the function of the middle ear by varying air pressure in the ear canal and measuring the movement of the eardrum. This helps detect fluid, ear infections, or eustachian tube dysfunction.
Process of a Hearing Test
-
Initial Consultation:
- Discussion of hearing concerns, medical history, and any symptoms the patient is experiencing.
-
Conducting the Tests:
- The audiologist performs a series of hearing tests based on the initial assessment and patient’s needs.
-
Interpreting Results:
- The audiologist reviews the results, explains the type and degree of hearing loss, and discusses potential treatment options.
Hearing Aids Fitting Service
Types of Hearing Aids
-
Behind-the-Ear (BTE):
- Sits behind the ear and is connected to an earmold or ear tip via a thin tube. Suitable for all degrees of hearing loss.
-
In-the-Ear (ITE):
- Custom-made to fit in the outer ear. Suitable for mild to severe hearing loss.
-
In-the-Canal (ITC) and Completely-in-the-Canal (CIC):
- Custom-made to fit partly or completely in the ear canal. Less visible and suitable for mild to moderately severe hearing loss.
-
Receiver-in-Canal (RIC) or Receiver-in-the-Ear (RITE):
- Similar to BTE but with the receiver placed in the ear canal. Suitable for mild to severe hearing loss.
Hearing Aids Fitting Process
-
Assessment and Selection:
- Based on the hearing test results, the audiologist recommends suitable hearing aids, considering the patient’s hearing loss, lifestyle, and preferences.
-
Ear Impressions:
- For custom hearing aids, the audiologist takes impressions of the ear canal to ensure a precise fit.
-
Hearing Aid Programming:
- The audiologist programs the hearing aids using specialized software to match the patient’s hearing loss profile.
-
Fitting and Adjustment:
- The patient tries on the hearing aids, and the audiologist makes adjustments to ensure comfort and optimal sound quality. This may include fine-tuning the volume, frequency settings, and other features.
-
Education and Training:
- The patient is educated on how to use, care for, and maintain the hearing aids. This includes inserting and removing the devices, changing batteries or charging them, and cleaning procedures.
-
Follow-Up Appointments:
- Scheduled visits to monitor the patient’s progress, address any issues, and make necessary adjustments to the hearing aids.
Benefits of Hearing Aids
- Improved Hearing: Enhanced ability to hear and understand speech, especially in noisy environments.
- Better Communication: Improved communication with family, friends, and colleagues, leading to a better quality of life.
- Increased Safety: Enhanced awareness of environmental sounds, such as alarms and traffic, improving safety.
- Mental Health: Reduction in feelings of isolation, anxiety, and depression associated with hearing loss.
Importance of Early Intervention
- Preventing Further Hearing Loss: Early detection and treatment can prevent further deterioration of hearing.
- Cognitive Health: Addressing hearing loss early can help prevent cognitive decline associated with untreated hearing loss.
- Enhanced Quality of Life: Improved hearing leads to better social interactions, job performance, and overall well-being.
Choosing the Right Provider
- Qualified Audiologists: Ensure services are provided by licensed and experienced audiologists.
- Comprehensive Care: Look for providers that offer a full range of services, from diagnosis to ongoing support and maintenance.
- Patient-Centered Approach: Choose a provider who prioritizes patient education, comfort, and satisfaction.
Hearing tests and hearing aids fitting services are crucial for individuals experiencing hearing loss. These services provide accurate diagnosis, effective treatment, and ongoing support to improve hearing and enhance quality of life.
